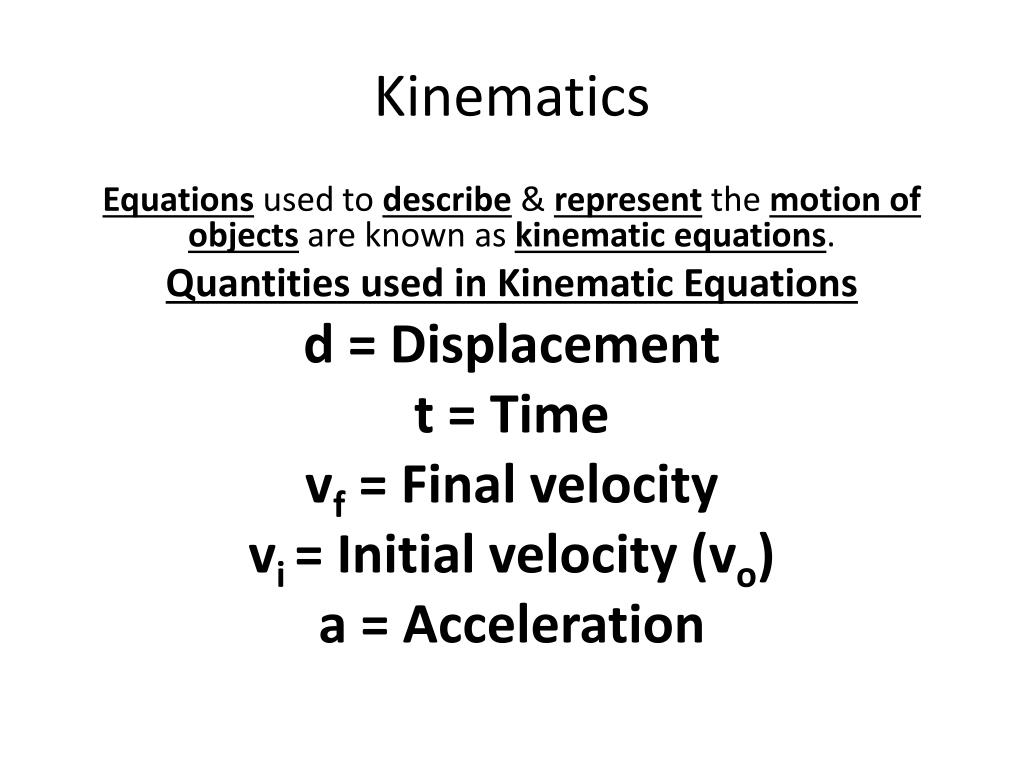
Final Velocity Kinematic Equation . kinematics equations is set of three equations which is used for motion in a straight line with constant acceleration. — kinematic equations describe the motion of objects under constant acceleration. There are four basic kinematics equations: — calculate final velocity of an accelerating object, given initial velocity, acceleration, and time. Each equation contains four variables. kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another. To learn how to solve problems with these new, longer. — kinematic equation 1: The first two equations of motion each describe one kinematic variable as a function of time. They relate displacement, velocity, acceleration, and time. An example is ( v = u + at ), where ( v ) is final velocity, ( u ) is initial velocity, ( a ) is acceleration, and ( t ) is time. Calculate displacement and final position of an accelerating object, given initial position, initial velocity, time, and acceleration. the variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi).
from www.tessshebaylo.com
— calculate final velocity of an accelerating object, given initial velocity, acceleration, and time. — kinematic equations describe the motion of objects under constant acceleration. kinematics equations is set of three equations which is used for motion in a straight line with constant acceleration. — kinematic equation 1: Each equation contains four variables. To learn how to solve problems with these new, longer. kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another. There are four basic kinematics equations: An example is ( v = u + at ), where ( v ) is final velocity, ( u ) is initial velocity, ( a ) is acceleration, and ( t ) is time. Calculate displacement and final position of an accelerating object, given initial position, initial velocity, time, and acceleration.
Kinematic Equation For Final Velocity Tessshebaylo
Final Velocity Kinematic Equation kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another. There are four basic kinematics equations: — kinematic equations describe the motion of objects under constant acceleration. They relate displacement, velocity, acceleration, and time. The first two equations of motion each describe one kinematic variable as a function of time. Each equation contains four variables. — calculate final velocity of an accelerating object, given initial velocity, acceleration, and time. the variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). An example is ( v = u + at ), where ( v ) is final velocity, ( u ) is initial velocity, ( a ) is acceleration, and ( t ) is time. To learn how to solve problems with these new, longer. Calculate displacement and final position of an accelerating object, given initial position, initial velocity, time, and acceleration. — kinematic equation 1: kinematics equations is set of three equations which is used for motion in a straight line with constant acceleration. kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another.
From www.youtube.com
Physics, Kinematics (7 of 7) 1 D Horizontal Motion, Solve for Final Final Velocity Kinematic Equation — kinematic equations describe the motion of objects under constant acceleration. Calculate displacement and final position of an accelerating object, given initial position, initial velocity, time, and acceleration. — calculate final velocity of an accelerating object, given initial velocity, acceleration, and time. There are four basic kinematics equations: Each equation contains four variables. They relate displacement, velocity, acceleration,. Final Velocity Kinematic Equation.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Kinematics Equations PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID Final Velocity Kinematic Equation — calculate final velocity of an accelerating object, given initial velocity, acceleration, and time. Calculate displacement and final position of an accelerating object, given initial position, initial velocity, time, and acceleration. kinematics equations is set of three equations which is used for motion in a straight line with constant acceleration. To learn how to solve problems with these. Final Velocity Kinematic Equation.
From www.youtube.com
Motion 6 The Kinematic Equations YouTube Final Velocity Kinematic Equation — calculate final velocity of an accelerating object, given initial velocity, acceleration, and time. To learn how to solve problems with these new, longer. kinematics equations is set of three equations which is used for motion in a straight line with constant acceleration. There are four basic kinematics equations: Each equation contains four variables. Calculate displacement and final. Final Velocity Kinematic Equation.
From www.tessshebaylo.com
Kinematic Equation Final Velocity Tessshebaylo Final Velocity Kinematic Equation Calculate displacement and final position of an accelerating object, given initial position, initial velocity, time, and acceleration. — kinematic equation 1: The first two equations of motion each describe one kinematic variable as a function of time. kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another. the variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final. Final Velocity Kinematic Equation.
From thirdspacelearning.com
Kinematics Formula GCSE Maths Steps, Examples & Worksheet Final Velocity Kinematic Equation There are four basic kinematics equations: — kinematic equation 1: — kinematic equations describe the motion of objects under constant acceleration. Each equation contains four variables. kinematics equations is set of three equations which is used for motion in a straight line with constant acceleration. kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another. They. Final Velocity Kinematic Equation.
From www.tessshebaylo.com
Kinematic Equation For Final Velocity Tessshebaylo Final Velocity Kinematic Equation They relate displacement, velocity, acceleration, and time. Each equation contains four variables. The first two equations of motion each describe one kinematic variable as a function of time. — kinematic equation 1: — calculate final velocity of an accelerating object, given initial velocity, acceleration, and time. kinematics equations is set of three equations which is used for. Final Velocity Kinematic Equation.
From www.youtube.com
Physics, Kinematics, Free Fall (10 of 12) Final Velocity at Bottom Final Velocity Kinematic Equation the variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). — kinematic equations describe the motion of objects under constant acceleration. Each equation contains four variables. — kinematic equation 1: An example is ( v = u + at ), where ( v ) is final velocity, ( u ) is. Final Velocity Kinematic Equation.
From exobagdsh.blob.core.windows.net
Velocity Gravity Height Equation at Staci Jennings blog Final Velocity Kinematic Equation They relate displacement, velocity, acceleration, and time. the variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). Calculate displacement and final position of an accelerating object, given initial position, initial velocity, time, and acceleration. There are four basic kinematics equations: The first two equations of motion each describe one kinematic variable as a. Final Velocity Kinematic Equation.
From quizdbcornwallis.z21.web.core.windows.net
What Is Final Velocity Final Velocity Kinematic Equation — calculate final velocity of an accelerating object, given initial velocity, acceleration, and time. To learn how to solve problems with these new, longer. kinematics equations is set of three equations which is used for motion in a straight line with constant acceleration. — kinematic equation 1: kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one. Final Velocity Kinematic Equation.
From www.inertialearning.com
Kinematic Equations IB Physics HL/SL Final Velocity Kinematic Equation Each equation contains four variables. — kinematic equations describe the motion of objects under constant acceleration. There are four basic kinematics equations: To learn how to solve problems with these new, longer. Calculate displacement and final position of an accelerating object, given initial position, initial velocity, time, and acceleration. the variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d),. Final Velocity Kinematic Equation.
From physicsteacher.in
Kinematics equations or motion equations cheat sheet or reckoner Final Velocity Kinematic Equation — calculate final velocity of an accelerating object, given initial velocity, acceleration, and time. Calculate displacement and final position of an accelerating object, given initial position, initial velocity, time, and acceleration. the variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). There are four basic kinematics equations: — kinematic equation 1:. Final Velocity Kinematic Equation.
From www.youtube.com
Kinematics Equations 1 Solving for Velocity YouTube Final Velocity Kinematic Equation Each equation contains four variables. kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another. kinematics equations is set of three equations which is used for motion in a straight line with constant acceleration. the variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). To learn how to solve problems with. Final Velocity Kinematic Equation.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED Using the rotational motion versions of the kinematic equations Final Velocity Kinematic Equation the variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). — calculate final velocity of an accelerating object, given initial velocity, acceleration, and time. There are four basic kinematics equations: — kinematic equation 1: kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another. Calculate displacement and final position of. Final Velocity Kinematic Equation.
From www.tessshebaylo.com
Kinematic Equation For Final Velocity Tessshebaylo Final Velocity Kinematic Equation — calculate final velocity of an accelerating object, given initial velocity, acceleration, and time. There are four basic kinematics equations: They relate displacement, velocity, acceleration, and time. — kinematic equations describe the motion of objects under constant acceleration. the variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). The first two. Final Velocity Kinematic Equation.
From www.animalia-life.club
Final Velocity Equation Final Velocity Kinematic Equation Calculate displacement and final position of an accelerating object, given initial position, initial velocity, time, and acceleration. To learn how to solve problems with these new, longer. They relate displacement, velocity, acceleration, and time. The first two equations of motion each describe one kinematic variable as a function of time. — calculate final velocity of an accelerating object, given. Final Velocity Kinematic Equation.
From www.youtube.com
The Kinematic Equations (Physics) YouTube Final Velocity Kinematic Equation An example is ( v = u + at ), where ( v ) is final velocity, ( u ) is initial velocity, ( a ) is acceleration, and ( t ) is time. kinematics equations is set of three equations which is used for motion in a straight line with constant acceleration. Calculate displacement and final position of. Final Velocity Kinematic Equation.
From owlcation.com
Uniform Acceleration Lesson Plan Description Conversion Owlcation Final Velocity Kinematic Equation — kinematic equations describe the motion of objects under constant acceleration. the variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). — calculate final velocity of an accelerating object, given initial velocity, acceleration, and time. kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another. There are four basic kinematics. Final Velocity Kinematic Equation.
From www.gauthmath.com
Solved A problem provides values for initial velocity, final velocity Final Velocity Kinematic Equation — kinematic equations describe the motion of objects under constant acceleration. The first two equations of motion each describe one kinematic variable as a function of time. There are four basic kinematics equations: Each equation contains four variables. — calculate final velocity of an accelerating object, given initial velocity, acceleration, and time. — kinematic equation 1: . Final Velocity Kinematic Equation.